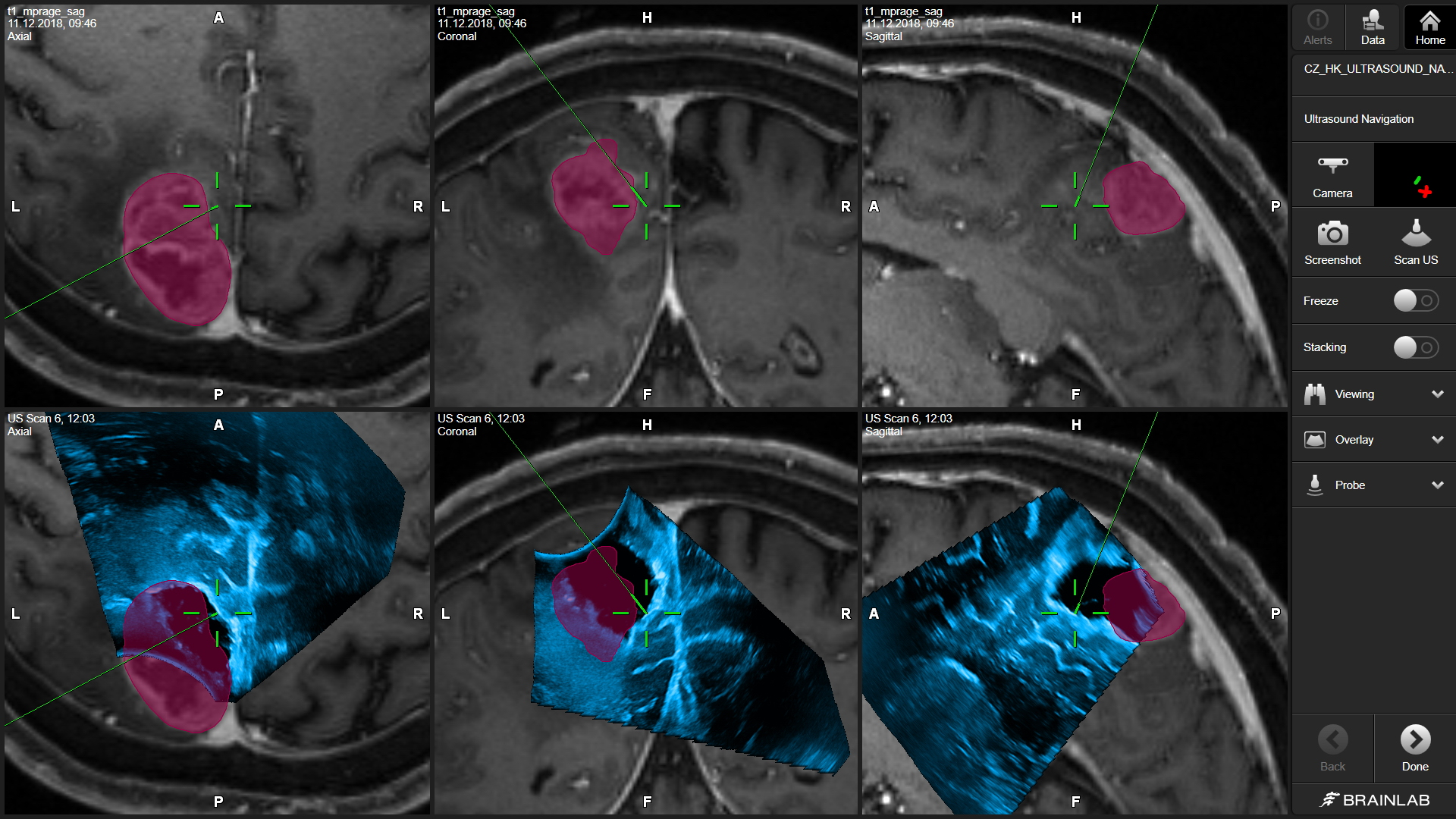
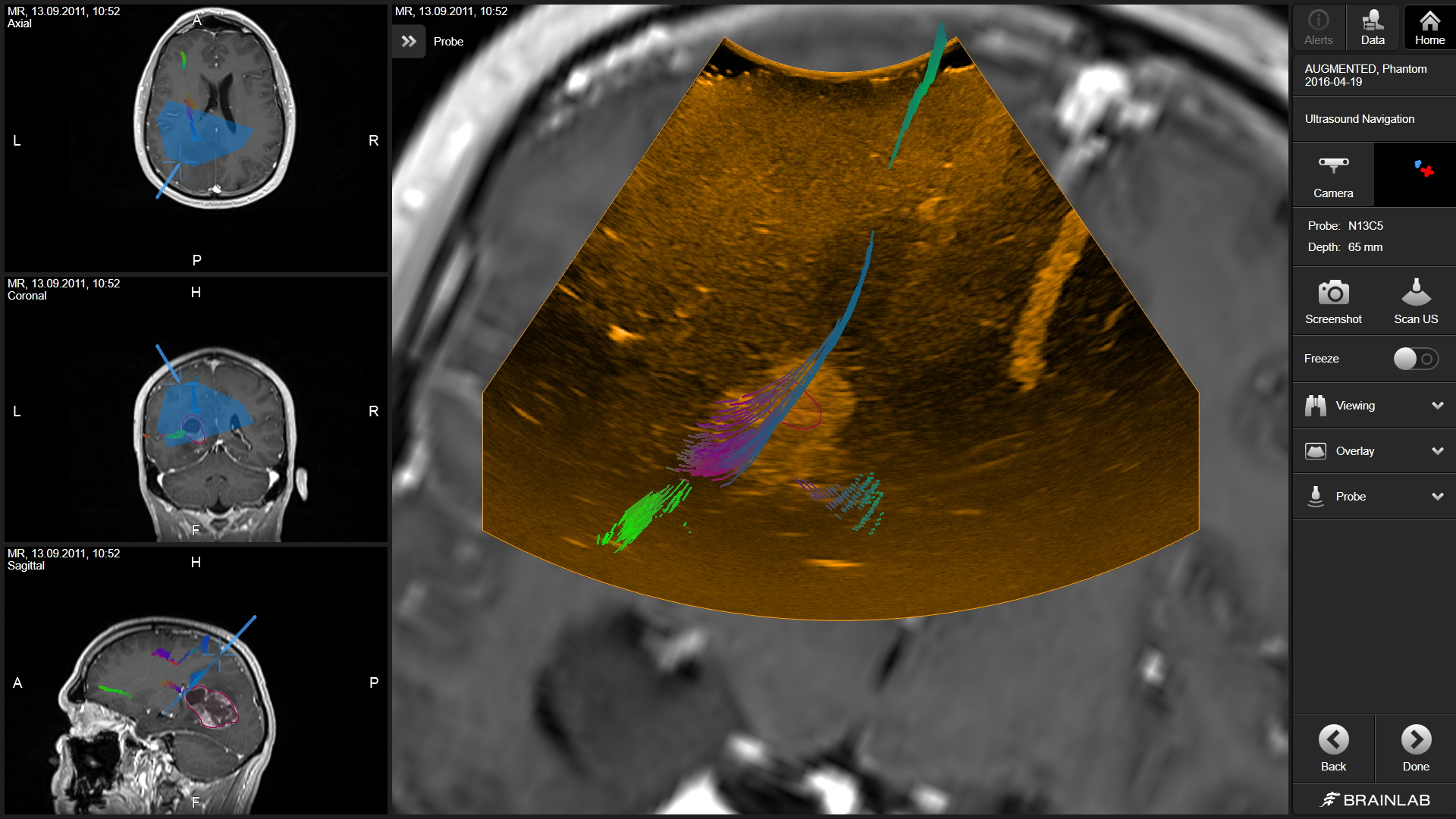
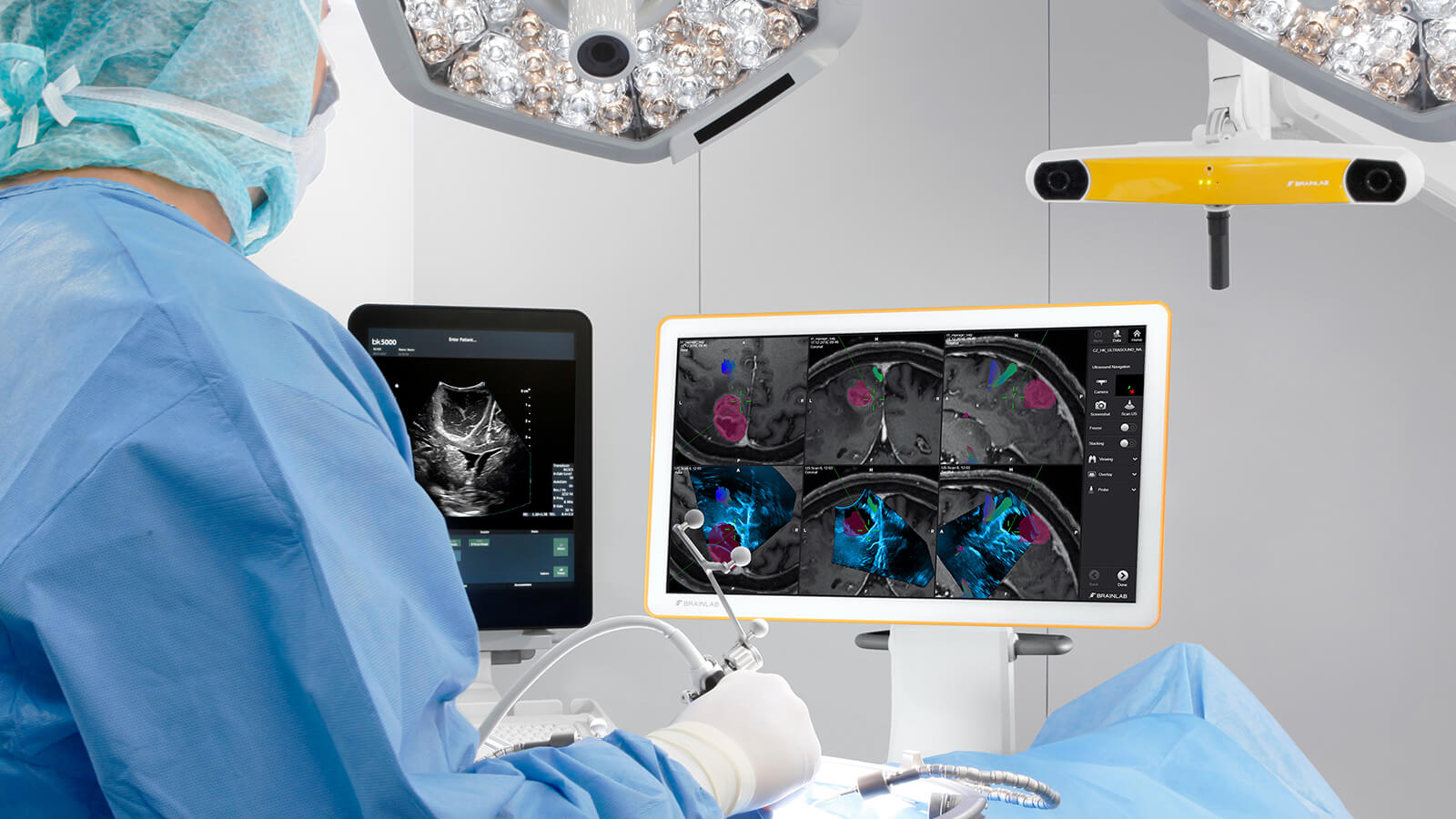
A whole new dimension. In real time. At any time. We’re delivering innovative, science-backed technology to help surgeons achieve their goal of maximum safe resection, even if brain shift or other navigational inaccuracies occur. We’re operationalizing ultrasound navigation in a new way, transforming this intraoperative imaging technology to deliver a dynamic layer of confidence.
Real-Time Correlation of
Intraoperative Ultrasound and Preop MRI
Forget everything you know about intraoperative ultrasound: Gain valuable real-time insights through the right orientation and instantaneous correlation between ultrasound and familiar preop MR images.
Precision and Confidence in
Navigating Cranial Resection Challenges
Gain the navigational accuracy you need to address the greatest challenges in cranial resection: Visualization of and compensation for brain shift; achievement of maximum safe resection and identification of residual tumor.
Efficient Intraoperative Imaging
Without Workflow Interruption
Take advantage of our cost-effective, fast and straightforward intraoperative imaging technology that will not interrupt your workflow.
Scientific One-pager
Discover more about the technique, clinical utility and benefits of Brainlab Ultrasound Navigation in neurosurgery.

Science that is making waves in the industry
Join the wave
Get the navigational accuracy you need to achieve your goals.
Peel back the layers of our
powerful technology
Take a deep dive
Check out the real-world evidence you need to make the shift.
Your new intraop imaging journey starts now
Maximize insights with science-backed Brainlab Ultrasound Navigation