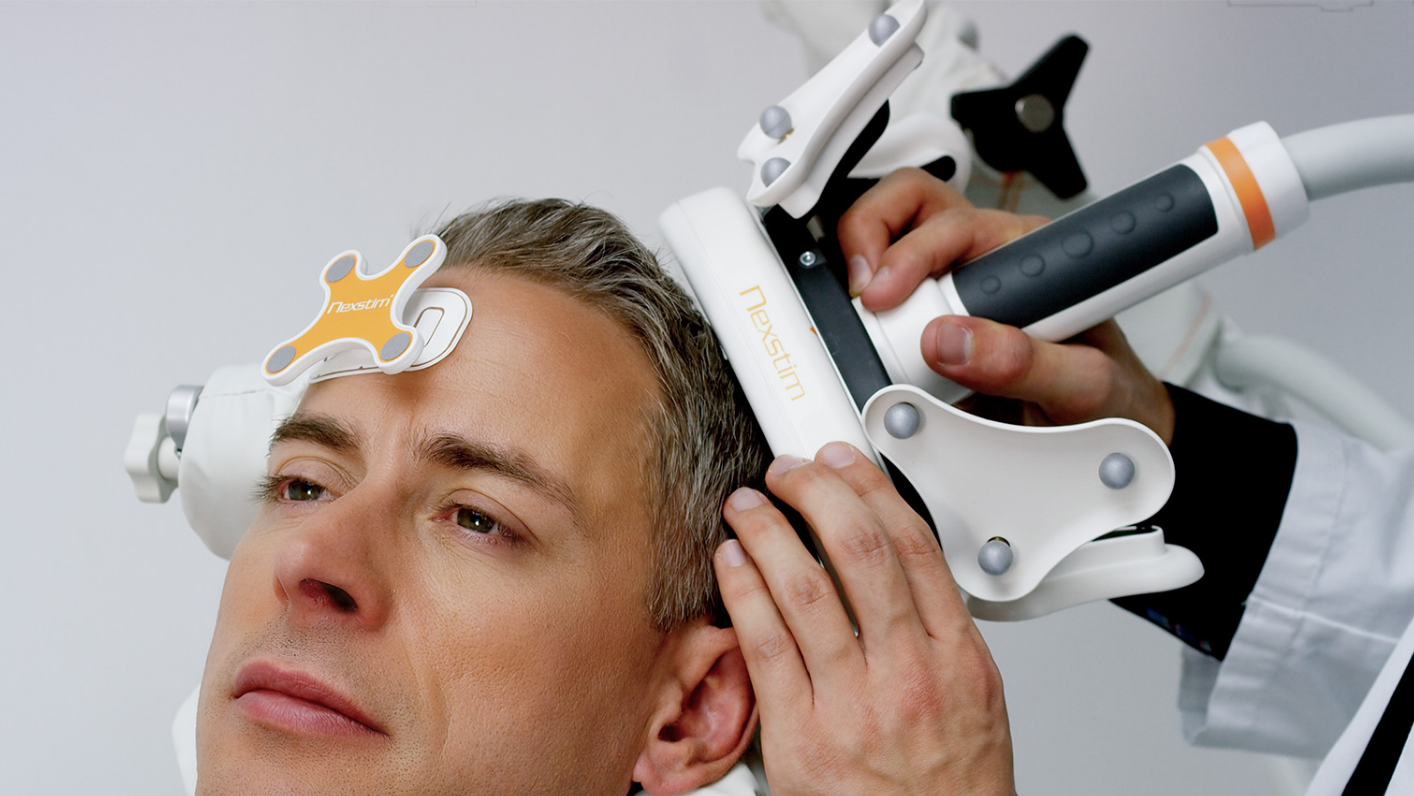
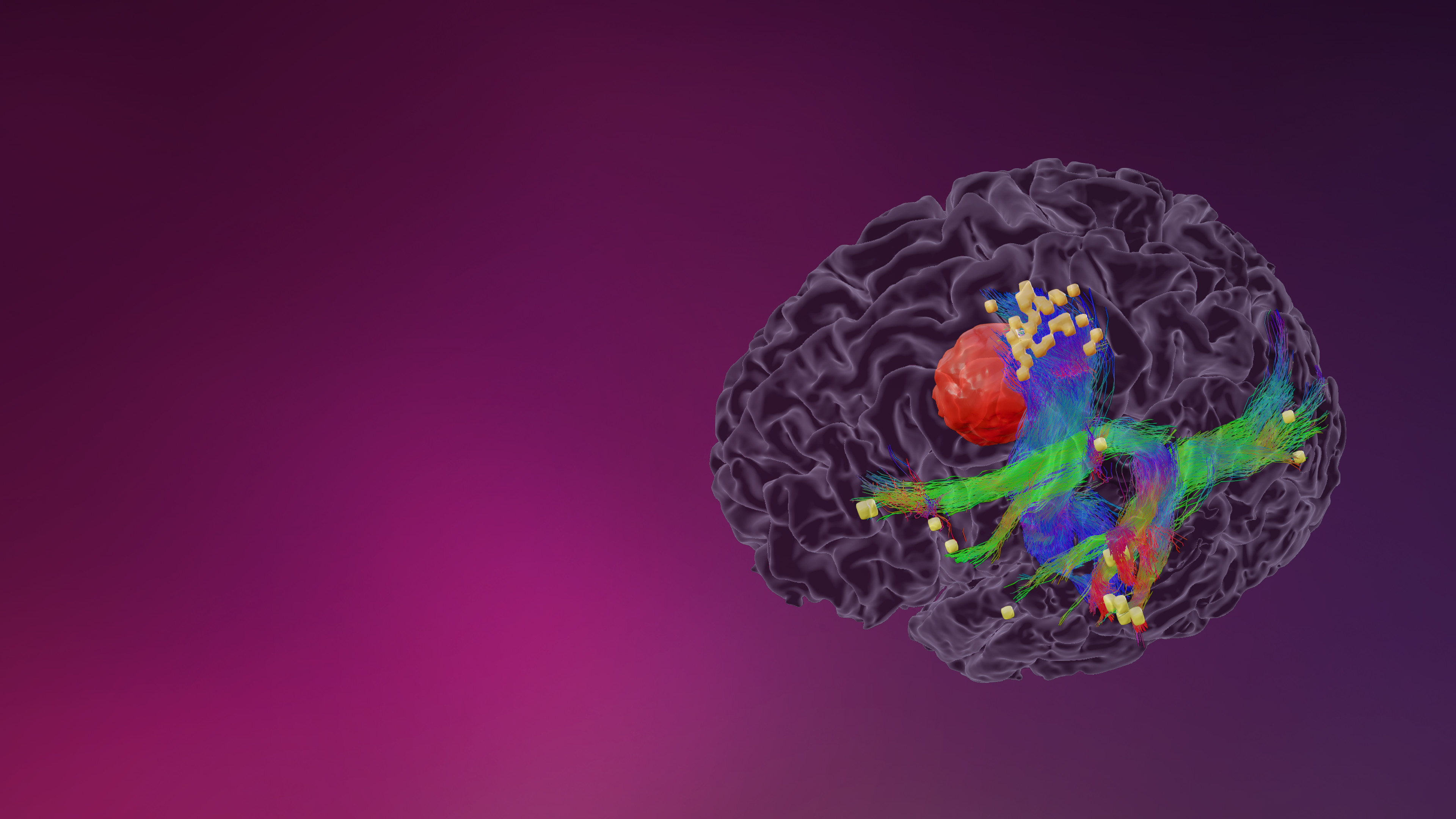
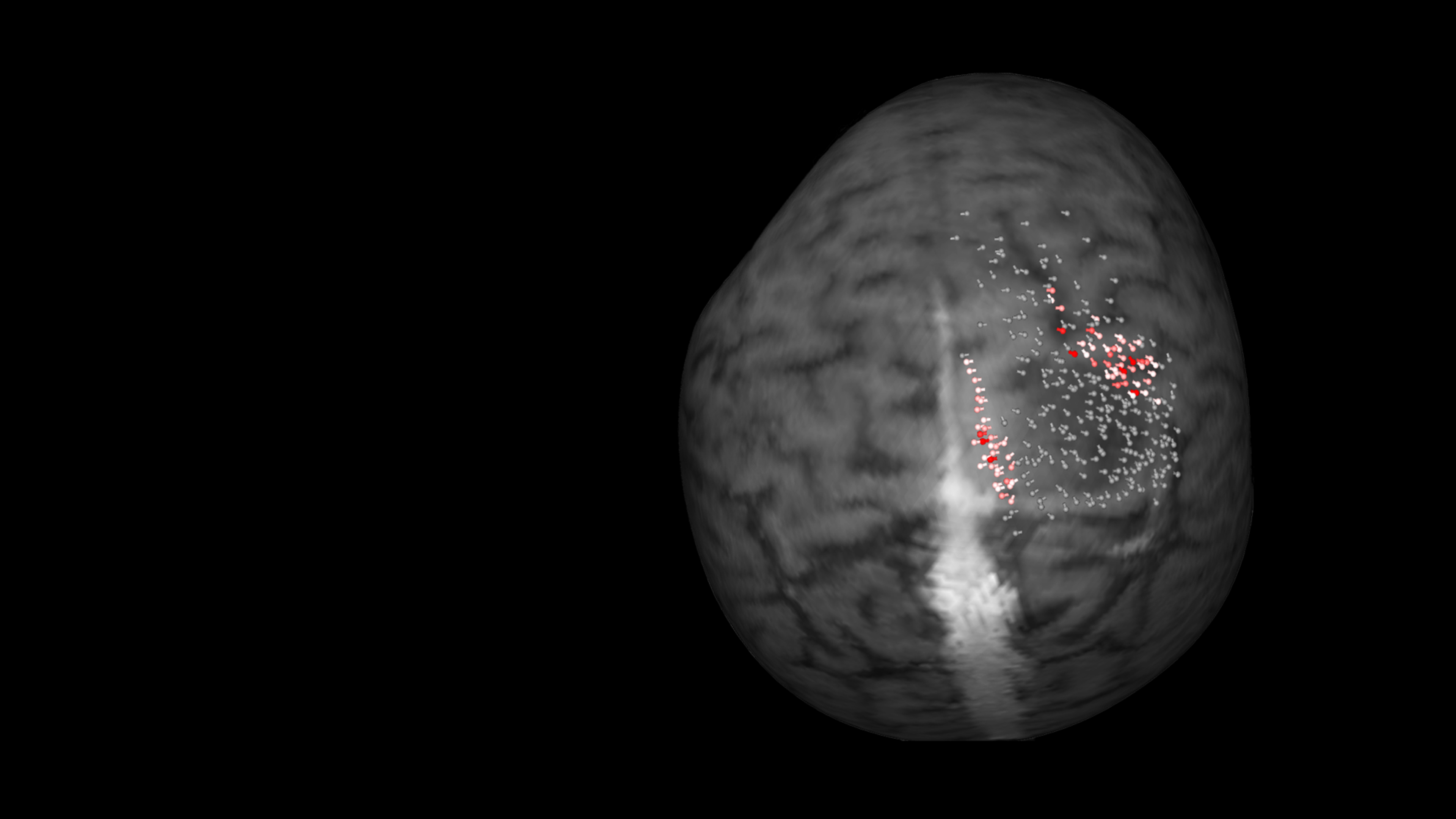
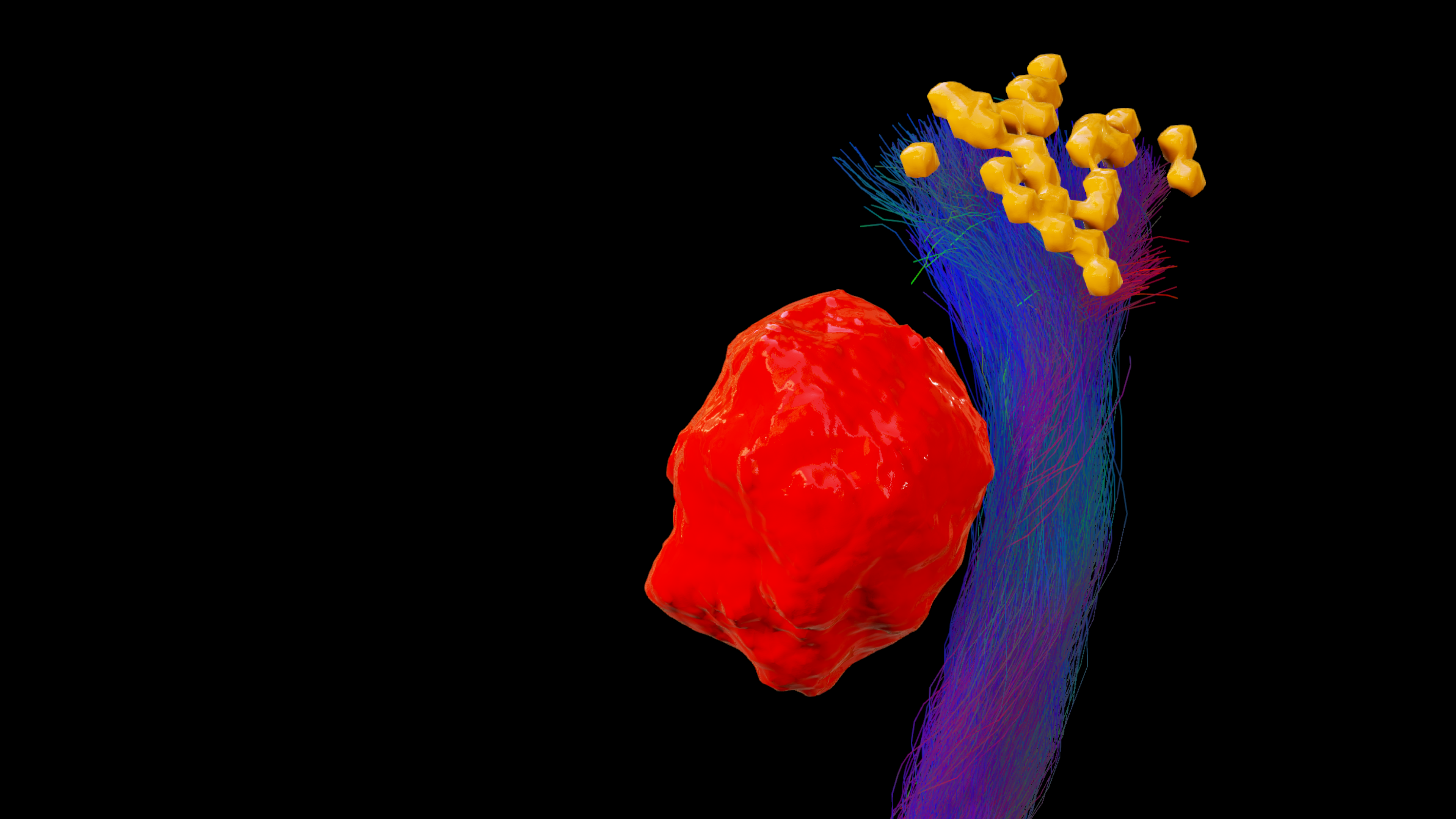
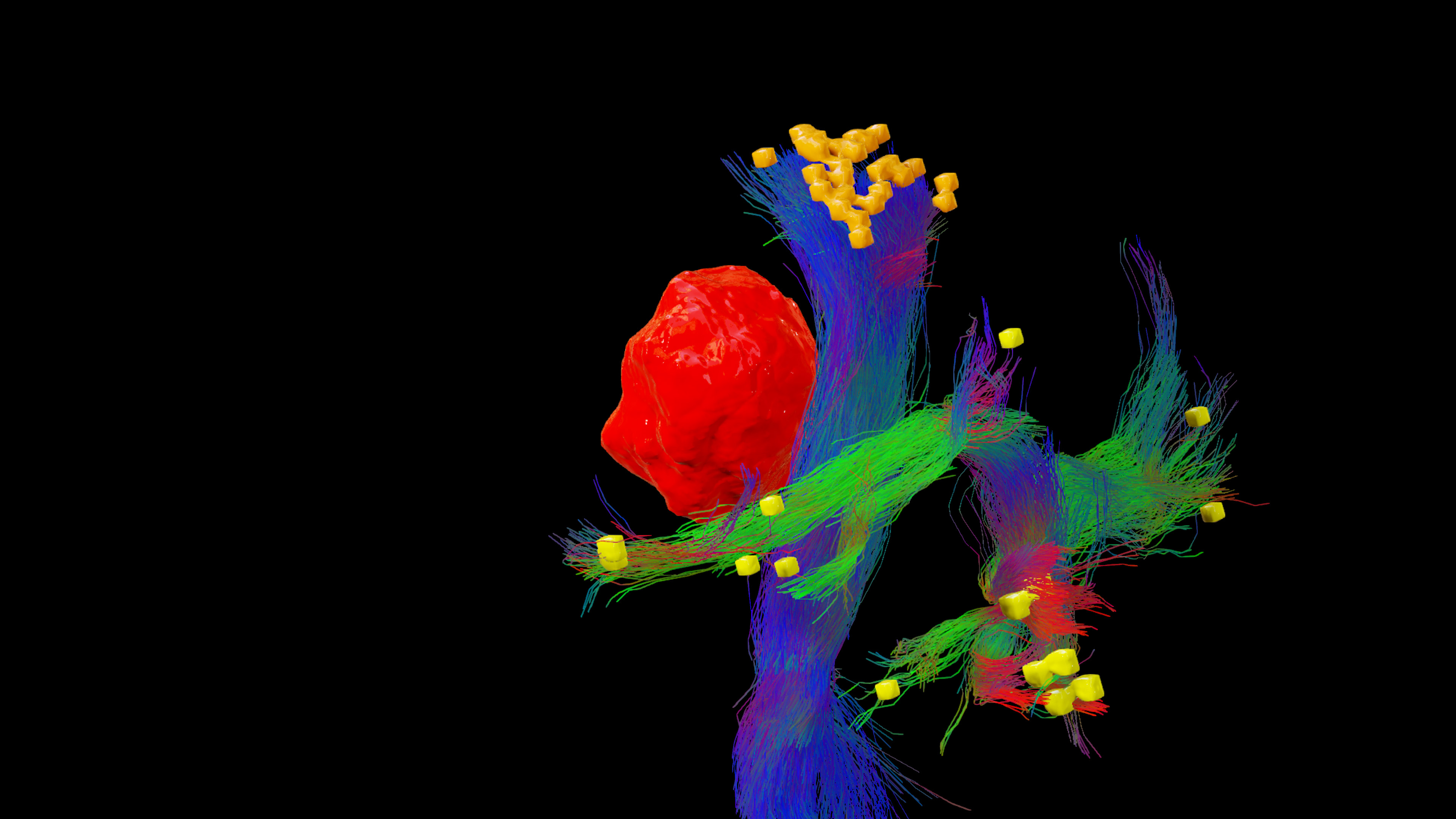
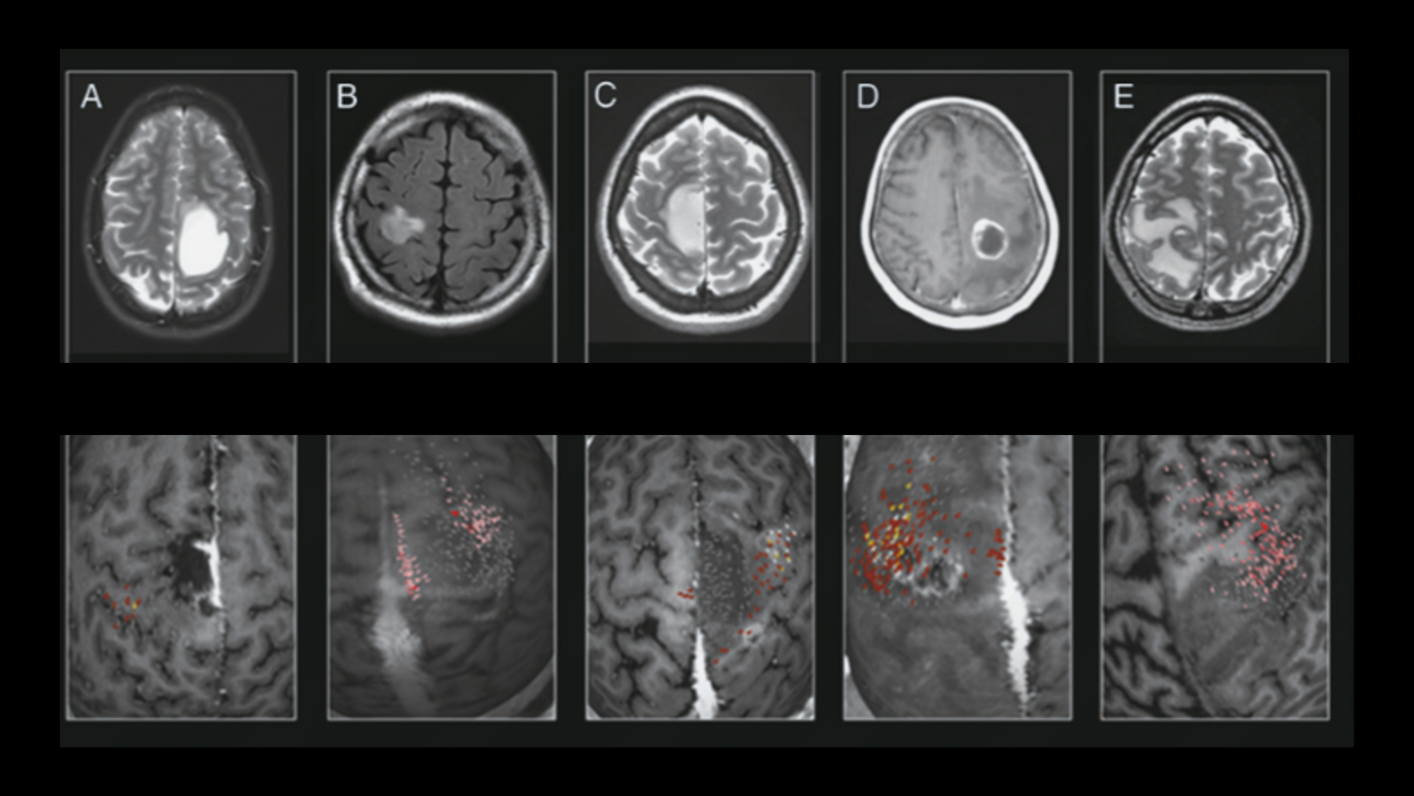
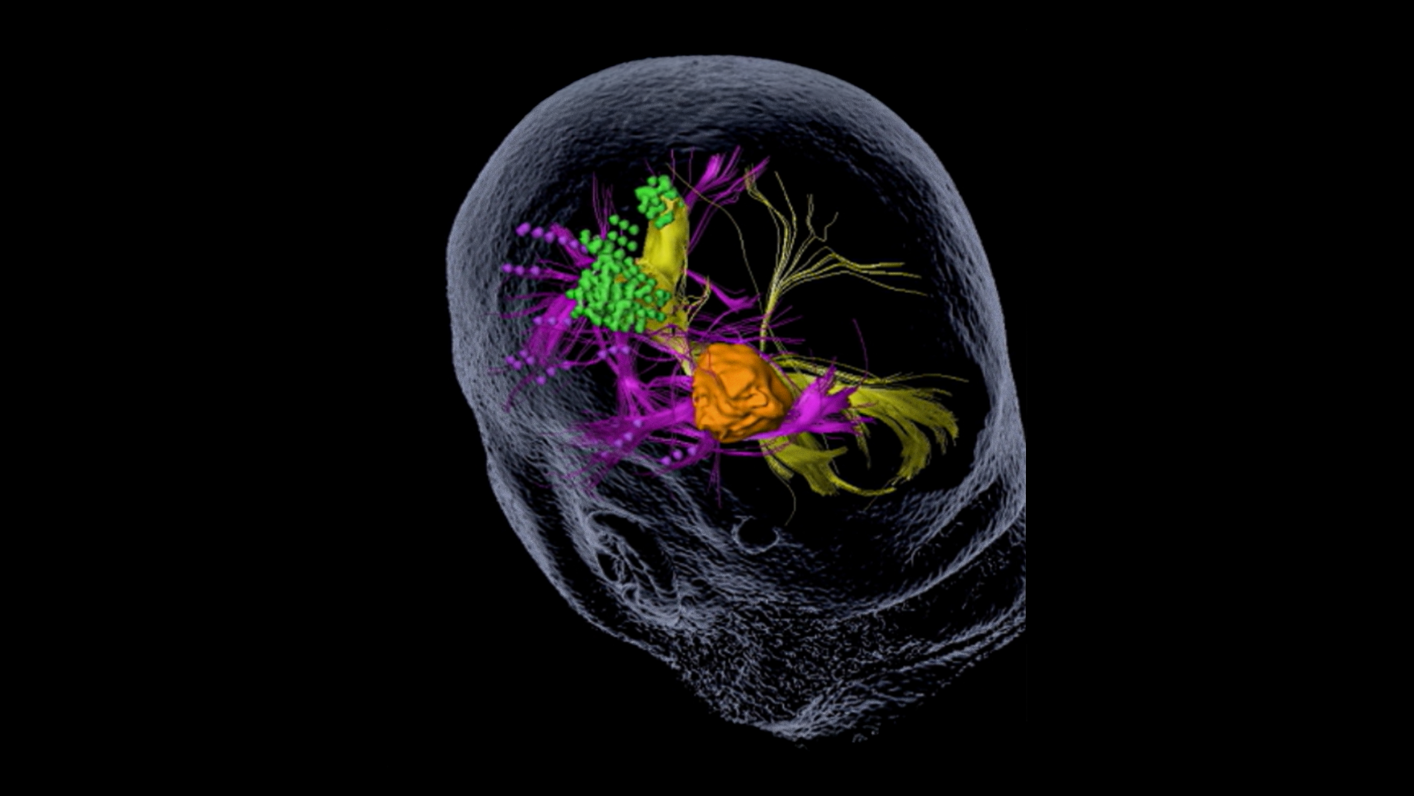
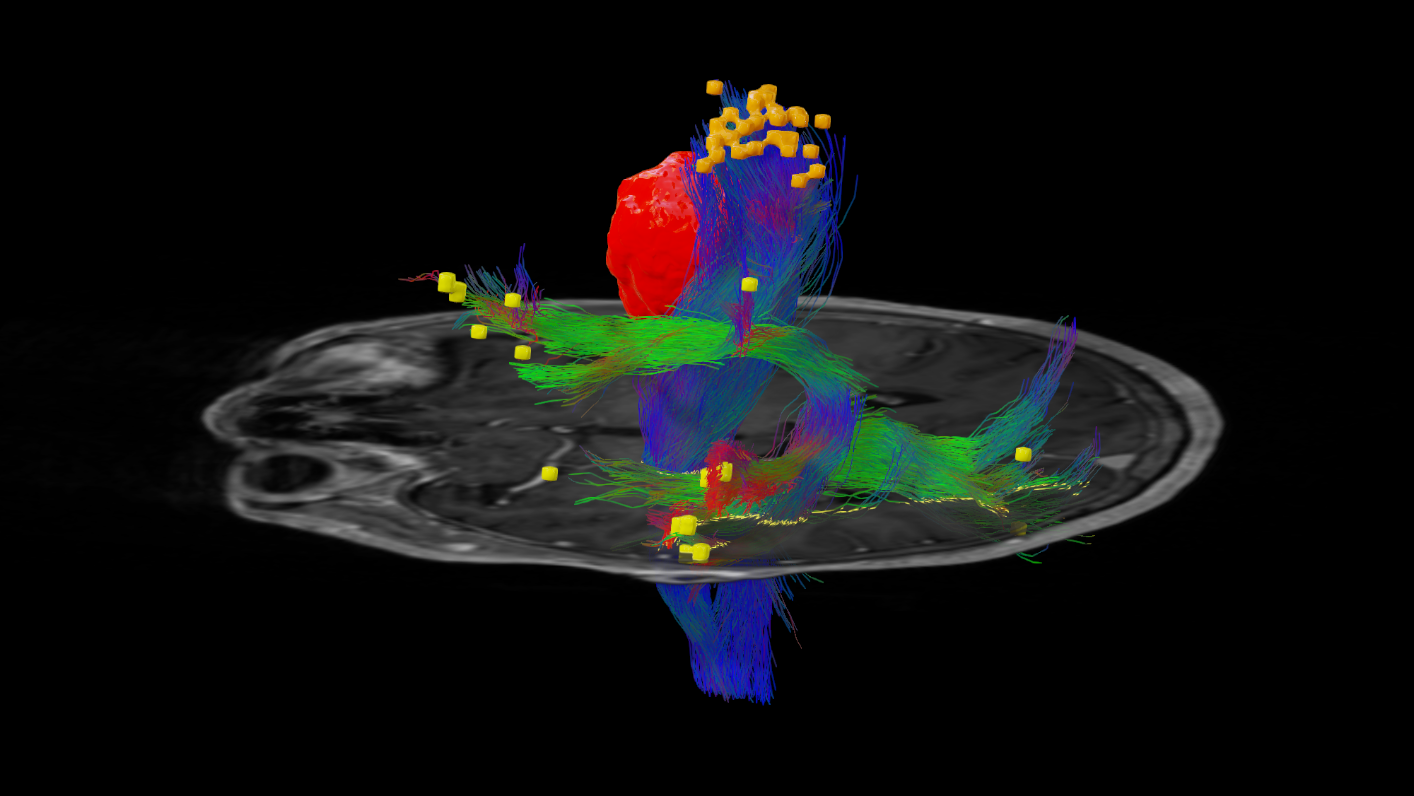
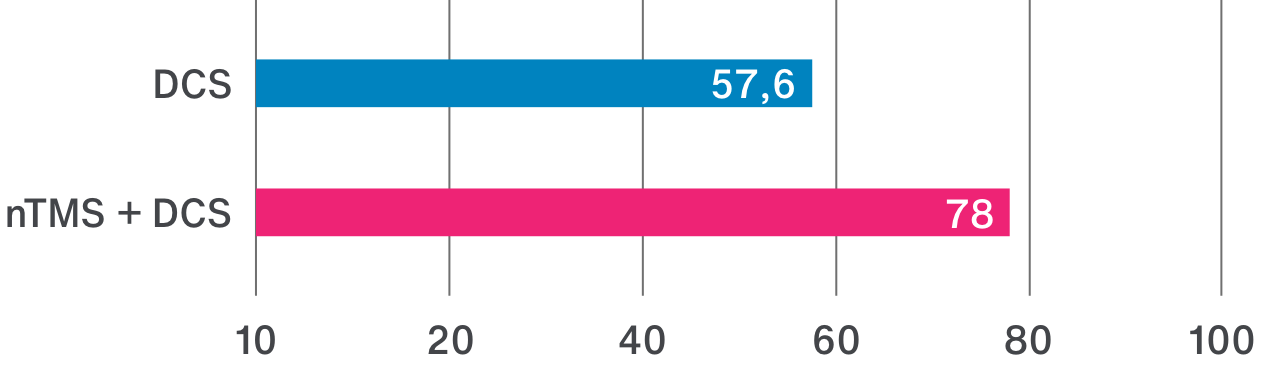
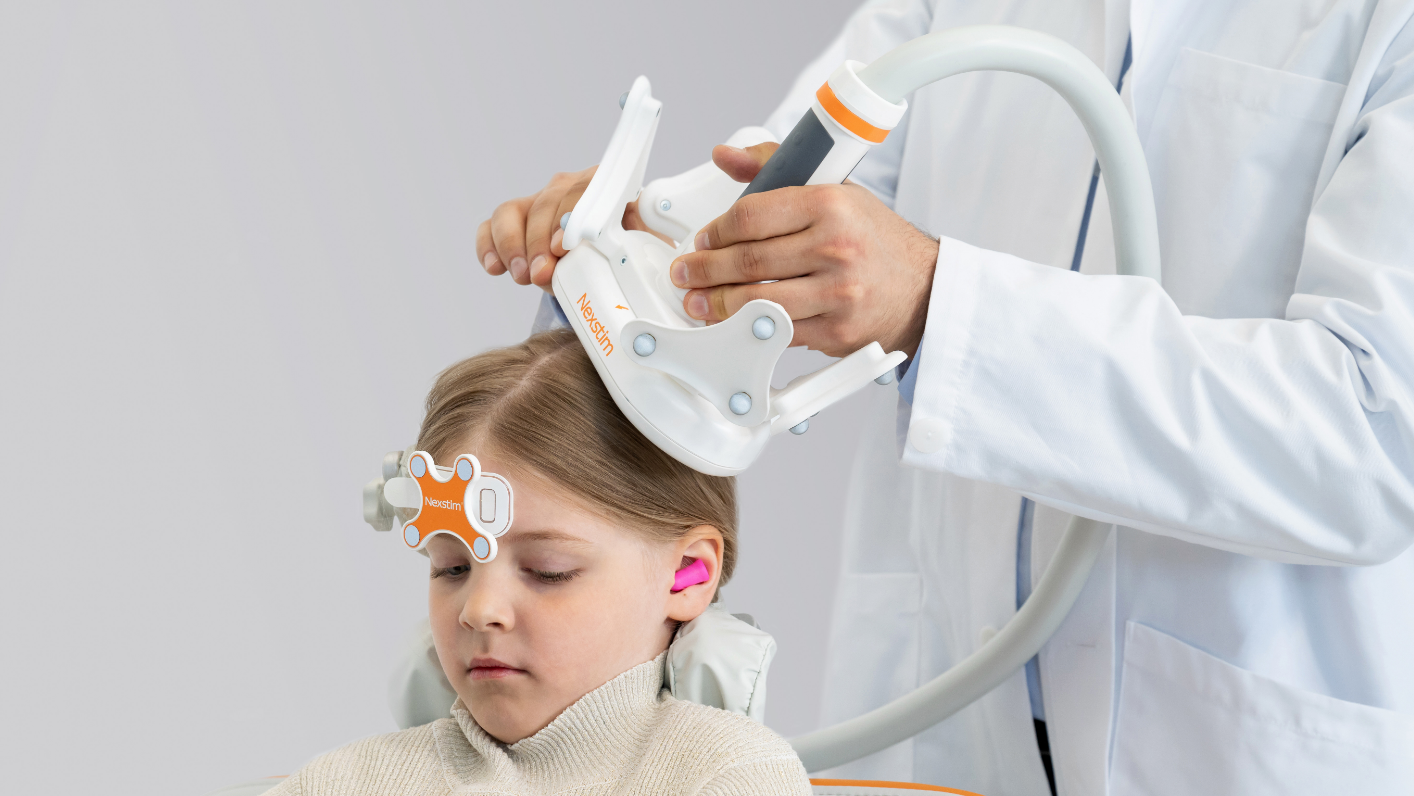
The location of motor or language functions may be unclear in tumor resection cases as lesions in the brain can cause functional reorganization in 40 – 50% of patients.4
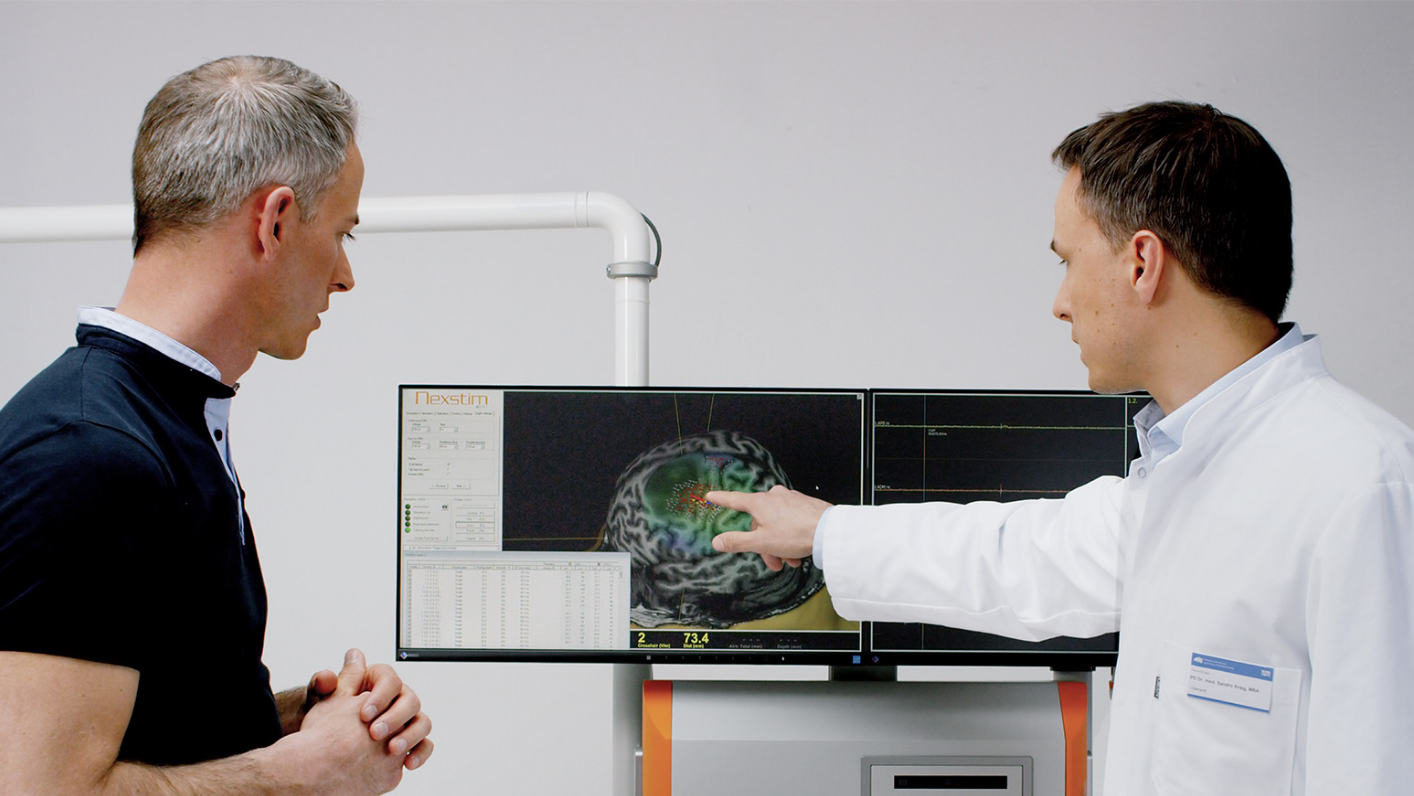
nTMS enables the visualization of lesion-induced functional reorganization.
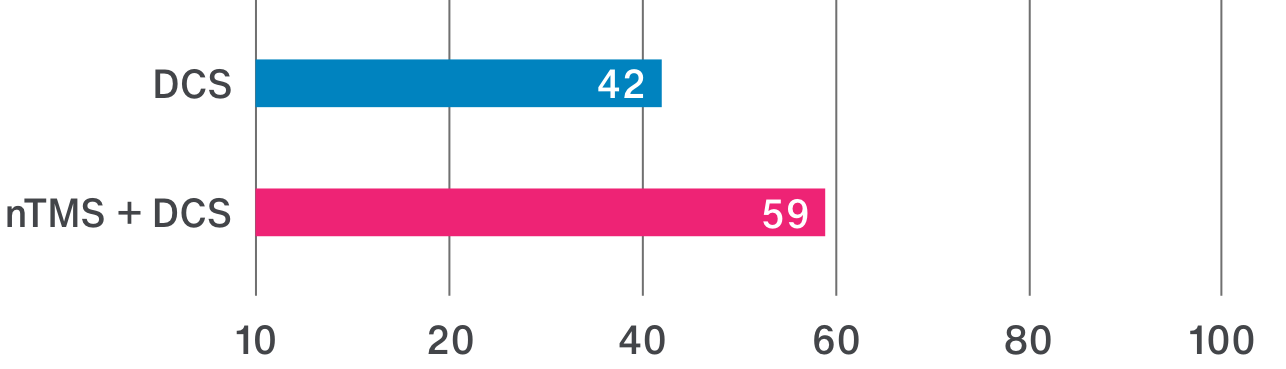
nTMS results allow clinicians to adapt treatment plans, offering a precise and patient-specific approach. By ruling out motor cortex involvement, tumors initially considered inoperable may be deemed suitable for surgery.3
Image source: Frey D., Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation improves the treatment outcome in patients with brain tumors in motor eloquent locations. Neuro Oncology 2014 Oct; 16(10): 1365–1372